* added note on importance of site_url this was in response to https://github.com/squidfunk/mkdocs-material/issues/4678#issuecomment-1327681673 * re-wording to say why site_url is always needed
8.1 KiB
Creating your site
After you've installed Material for MkDocs, you can bootstrap your project
documentation using the mkdocs executable. Go to the directory where you want
your project to be located and enter:
mkdocs new .
Alternatively, if you're running Material for MkDocs from within Docker, use:
=== "Unix, Powershell"
```
docker run --rm -it -v ${PWD}:/docs squidfunk/mkdocs-material new .
```
=== "Windows (cmd)"
```
docker run --rm -it -v "%cd%":/docs squidfunk/mkdocs-material new .
```
This will create the following structure:
.
├─ docs/
│ └─ index.md
└─ mkdocs.yml
Configuration
Minimal configuration
Simply set the site_name and add the following lines to mkdocs.yml to enable the theme:
site_name: My site
site_url: https://mydomain.org/mysite
theme:
name: material
The site_url setting is important for a number of reasons.
By default, MkDocs will assume that your site is hosted at the root of
your domain. This is not the case, for example, when publishing to GitHub
pages - unless you use a custom domain. Another reason is that some of the
plugins require the site_url to be set, so you should always do this.
???+ tip "Recommended: configuration validation and auto-complete"
In order to minimize friction and maximize productivity, Material for MkDocs
provides its own [schema.json][^1] for `mkdocs.yml`. If your editor supports
YAML schema validation, it's definitely recommended to set it up:
=== "Visual Studio Code"
1. Install [`vscode-yaml`][vscode-yaml] for YAML language support.
2. Add the schema under the `yaml.schemas` key in your user or
workspace [`settings.json`][settings.json]:
``` json
{
"yaml.schemas": {
"https://squidfunk.github.io/mkdocs-material/schema.json": "mkdocs.yml"
},
"yaml.customTags": [ // (1)!
"!ENV scalar",
"!ENV sequence",
"!relative scalar",
"tag:yaml.org,2002:python/name:material.extensions.emoji.to_svg",
"tag:yaml.org,2002:python/name:material.extensions.emoji.twemoji",
"tag:yaml.org,2002:python/name:pymdownx.superfences.fence_code_format"
]
}
```
1. This setting is necessary if you plan to use [icons and emojis],
or Visual Studio Code will show errors on certain lines.
=== "Other"
1. Ensure your editor of choice has support for YAML schema validation.
2. Add the following lines at the top of `mkdocs.yml`:
``` yaml
# yaml-language-server: $schema=https://squidfunk.github.io/mkdocs-material/schema.json
```
Advanced configuration
Material for MkDocs comes with many configuration options. The setup section explains in great detail how to configure and customize colors, fonts, icons and much more:
- Changing the colors
- Changing the fonts
- Changing the language
- Changing the logo and icons
- Ensuring data privacy
- Setting up navigation
- Setting up site search
- Setting up site analytics
- Setting up social cards
- Setting up a blog
- Setting up tags
- Setting up versioning
- Setting up the header
- Setting up the footer
- Adding a git repository
- Adding a comment system
- Building an optimized site
- Building for offline usage
Furthermore, see the list of supported Markdown extensions that are natively integrated with Material for MkDocs, delivering an unprecedented low-effort technical writing experience.
Previewing as you write
MkDocs includes a live preview server, so you can preview your changes as you write your documentation. The server will automatically rebuild the site upon saving. Start it with:
mkdocs serve # (1)!
-
If you have a large documentation project, it might take minutes until MkDocs has rebuilt all pages for you to preview. If you're only interested in the current page, the
--dirtyreloadflag will make rebuilds much faster:mkdocs serve --dirtyreload
If you're running Material for MkDocs from within Docker, use:
=== "Unix, Powershell"
```
docker run --rm -it -p 8000:8000 -v ${PWD}:/docs squidfunk/mkdocs-material
```
=== "Windows"
```
docker run --rm -it -p 8000:8000 -v "%cd%":/docs squidfunk/mkdocs-material
```
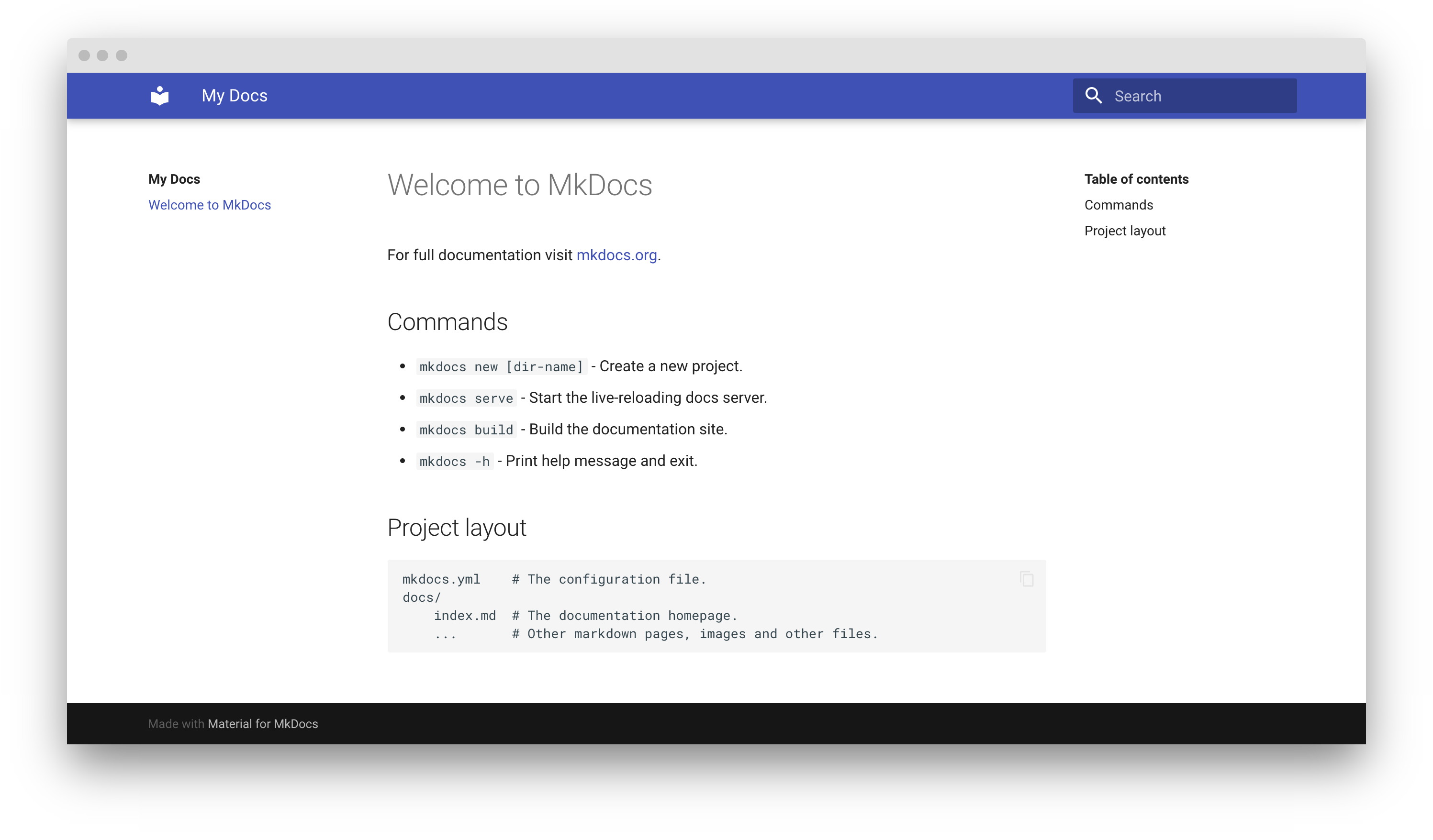
Point your browser to localhost:8000 and you should see:
Building your site
When you're finished editing, you can build a static site from your Markdown files with:
mkdocs build
If you're running Material for MkDocs from within Docker, use:
=== "Unix, Powershell"
```
docker run --rm -it -v ${PWD}:/docs squidfunk/mkdocs-material build
```
=== "Windows"
```
docker run --rm -it -v "%cd%":/docs squidfunk/mkdocs-material build
```
The contents of this directory make up your project documentation. There's no need for operating a database or server, as it is completely self-contained. The site can be hosted on GitHub Pages, GitLab Pages, a CDN of your choice or your private web space.
If you intend to distribute your documentation as a set of files to be
read from a local filesystem rather than a web server (such as in a
.zip file), please read the notes about building for offline
usage.